Securing the Future: Key Cloud Security Trends for 2025
As cloud computing continues its meteoric rise, security remains a top priority for organizations worldwide. Businesses are increasingly migrating workloads to the cloud, leveraging multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments for agility and scalability. However, this rapid adoption comes with heightened security challenges.
Emerging Cloud Security Trends 2025 indicate that organizations must prioritize zero-trust security models, AI-driven threat detection, and cloud-native security solutions to combat evolving risks. According to Gartner, by 2025, 99% of cloud security failures will be the customer’s fault, primarily due to misconfigurations and human error. Meanwhile, Forrester predicts that cyber threats targeting cloud environments will increase by 300%, with Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and AI-driven attacks leading the charge.
To stay ahead, businesses must embrace automated compliance frameworks, advanced encryption techniques, and identity-centric security strategies to safeguard cloud environments against next-generation cyber threats
In response, the security landscape is evolving, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as AI, Zero Trust, Cloud-Native Security, and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) to build resilient defenses. Companies like Check Point, in partnership with Cloud Security Services via Engro, are driving innovation to safeguard enterprises against modern cyber threats.
Let’s dive into the key trends shaping cloud security in 2025.
1. AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming cloud security by enhancing threat detection and response mechanisms. These technologies process vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that could indicate potential cyber threats. Unlike traditional security measures, which often react after an attack, AI-driven cloud security solutions proactively analyze behaviours, predict cyberattacks, and mitigate risks before they cause damage.
Machine Learning algorithms continuously learn from past incidents, improving their accuracy in distinguishing between normal activities and malicious actions. AI-powered security tools also enable automated responses, reducing the time needed to counter threats and minimizing human intervention.
With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats targeting cloud environments, AI and ML provide organizations with a robust, adaptive defense system. By leveraging these advanced technologies, businesses can strengthen their security posture, prevent breaches, and ensure a safer cloud infrastructure in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
AI-Powered Threat Detection and Response
Check Point, in partnership with Engro's Cloud Security Services, delivers a prevention-first approach to cybersecurity, ensuring robust protection against evolving threats. Utilizing Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR) technology, all files and attachments are meticulously inspected, malicious content is removed, and only clean, secure versions are delivered to users or inboxes. This proactive security framework safeguards organizations with seamless, real-time threat prevention, reinforcing a resilient and secure digital environment.
Traditional security measures struggle to keep up with the sophistication of modern cyber threats. Check Point’s GenAI Security uses AI-driven analytics to detect and neutralize threats autonomously, reducing response time from hours to seconds. AI-powered Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs) further strengthen defenses by providing deep visibility into cloud environments.
The Role of Generative AI in Security Automation
Generative AI is being integrated into Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms to automate threat analysis and response workflows. Forrester reports that 75% of security teams will rely on AI-powered automation by 2025, significantly reducing human intervention and improving efficiency.
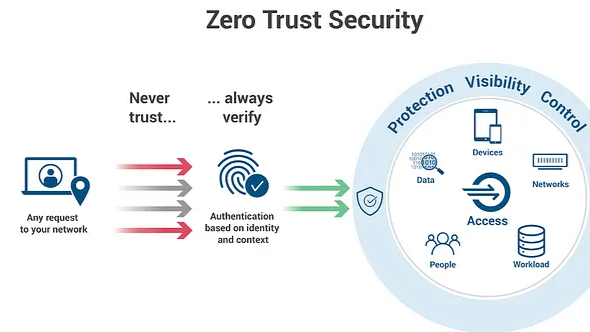
2. Zero Trust Architecture Becomes the Standard
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has evolved from a best practice to a critical security requirement. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, organizations are rapidly adopting zero trust in cloud security to enforce stringent access controls, authenticate every user and device, and eliminate implicit trust.
Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within the network, ZTA continuously verifies identities, monitors activity, and restricts access based on least privilege. This proactive approach minimizes attack surfaces, prevents lateral movement, and enhances overall cloud security. With increasing regulatory compliance requirements and the rise of remote work, Zero Trust is now a fundamental pillar of modern cybersecurity.
Implementation Challenges and Benefits
Zero Trust requires continuous identity verification, micro-segmentation, and strict least-privilege access policies. Check Point’s Zero Trust Security Best Practices emphasize the use of Identity and Access Management (IAM), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to minimize attack surfaces.
Case Study: Zero Trust in Action
A recent case study by Check Point highlighted how a global enterprise reduced unauthorized access incidents by 40% within six months of deploying a Zero Trust framework. By integrating Cloud Security Services via Engro, the company achieved end-to-end visibility across its multi-cloud infrastructure.
3. Rise of Cloud-Native Security Solutions
Traditional security models are ill-equipped to safeguard modern, dynamic cloud environments. As cloud adoption accelerates, businesses are shifting towards Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs) to secure workloads effectively. These platforms provide comprehensive security for serverless computing, containers, and Kubernetes clusters, addressing vulnerabilities in real time.
Unlike legacy security models, CNAPPs offer deep visibility, automated threat detection, and compliance management tailored for cloud-native architectures. With cyber threats evolving rapidly, organizations must embrace CNAPPs to protect their cloud assets, reduce attack surfaces, and enhance security postures without compromising agility or scalability. The future of cloud security lies in cloud-native protection.
Securing Cloud-Native Environments
Check Point Cloud Guard (CNAPP) provides comprehensive protection for cloud workloads, ensuring security, compliance, and preventing misconfigurations. As cloud environments become more complex, enterprises require robust security solutions to safeguard applications and data.
According to Gartner, 80% of enterprises will adopt Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs) by 2025 to enhance cloud security, streamline compliance, and mitigate risks. Cloud Guard CNAPP integrates advanced threat prevention, posture management, and runtime protection, offering a unified approach to securing serverless, containerized, and multi-cloud environments. By adopting CNAPP, organizations can proactively defend against evolving threats while maintaining operational efficiency and regulatory compliance in the cloud.
4. The Growing Threat of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) to exploit cloud workloads. Attackers use automated tools to deploy ransomware across cloud environments, demanding exorbitant ransoms from victims.
Prevention Strategies
Organizations are adopting Immutable Backups, Threat Intelligence, and AI-driven anomaly detection to counter RaaS threats. Check Point Cyber Security Report states that ransomware attacks on cloud environments surged by 95% in 2024, emphasizing the urgency for robust security measures.
5. Security for Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Environments
As enterprises embrace multi-cloud strategies, managing security across diverse cloud environments becomes a significant challenge. Each cloud provider comes with unique security protocols, compliance requirements, and configurations, making it difficult to maintain a unified security posture. Hybrid cloud environments further complicate this, as organizations must secure both on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure while ensuring seamless integration.
Without proper visibility and governance, security gaps can emerge, increasing the risk of cyber threats. To mitigate these challenges, businesses need Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions that provide continuous monitoring, compliance enforcement, and automated risk remediation across multiple cloud platforms.
Challenges and Solutions
Managing identity governance, data security, and workload protection across multiple cloud providers is challenging. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions like Check Point Harmony Cloud Security help organizations maintain compliance, detect misconfigurations, and enforce security policies.
Why Multi-Cloud Security Matters?
According to Forrester, 92% of enterprises now operate in multi-cloud environments, underscoring the critical need for unified security frameworks.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy Challenges
With the rapid evolution of data privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and India’s DPDP Act, regulatory compliance has become a top priority for cloud security teams. Organizations must navigate complex legal frameworks while ensuring their cloud environments remain secure and compliant. Failure to meet these regulations can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
As data protection laws become more stringent, businesses must adopt Security-as-Code practices, automate compliance processes, and implement robust cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions. Staying ahead of regulatory changes will be crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining trust in cloud ecosystems.
Automating Compliance with Security-as-Code
Security-as-Code (SaC) integrates compliance policies into DevOps pipelines, ensuring real-time adherence to regulatory frameworks. Check Point’s Cloud Security Compliance Guide emphasizes the importance of automating security configurations to reduce compliance violations by 60%.
Preparing for Stricter Regulations
By 2025, cloud providers will introduce stricter compliance measures. Businesses leveraging Check Point’s cloud security solutions via Engro can proactively address regulatory challenges, avoiding hefty fines.
7. The Future of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) in Cloud Security
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is revolutionizing cloud security by combining network and security functions into a unified, cloud-delivered framework. As organizations increasingly adopt remote work and multi-cloud environments, SASE ensures secure, seamless connectivity by integrating Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Web Gateways (SWG), Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS), and Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB).
This approach enhances security, reduces complexity, and improves performance by enforcing policies at the edge. With cyber threats evolving, businesses are turning to SASE to safeguard cloud workloads, prevent data breaches, and provide consistent security for users and applications—no matter where they are.
The Rise of SASE
SASE converges SD-WAN and Zero Trust, providing cloud-delivered security with enhanced network performance. Check Point SASE Security is leading the charge, offering seamless integration with cloud infrastructures.
Market Growth Predictions
Gartner forecasts that 70% of enterprises will adopt SASE by 2025, driven by the demand for secure remote access and streamlined security operations.
Conclusion
By 2025, cloud security trends will be driven by AI-powered automation, Zero Trust frameworks, cloud-native security, and the rise of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). As cyber threats become more advanced, businesses must take a proactive approach to protect their cloud environments.
Check Point, in collaboration with Engro's Cloud Security Services, delivers cutting-edge solutions tailored to address the complexities of modern security threats with precision and efficiency. Leveraging AI, automation, and regulatory compliance frameworks, organizations can enhance their security posture and stay ahead of cyber risks.
Future-proofing cloud security isn’t just about defense—it’s about smart, adaptive protection that evolves with threats. With intelligent automation and cutting-edge strategies, businesses can secure their cloud infrastructures more effectively than ever.
Are you prepared for the future of cloud security trends 2025? Now is the time to adopt the next generation of cybersecurity solutions and build a resilient, secure digital ecosystem.